
Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) is a novel approach to large-scale 3D printing that employs pelletized plastic feedstock rather than standard filament, it also called pellet 3D printing in AM industry. It enables large-scale manufacturing by employing pelletized plastic feedstock rather than standard filament. FGF is noted for its cost-effectiveness and capacity to create larger parts fast, serving sectors ranging from construction to automotive.
What is fused granulate fabrication (FGF)?
FGF works on a basic principle: plastic granules are fed into a barrel and screw extrusion system, melted, and deposited layer by layer to make an item. This contrasts from Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), which employs a filament spool. FGF is designed to handle large-format projects easily, making it an important tool for sectors that require fast and scalable manufacturing solutions.
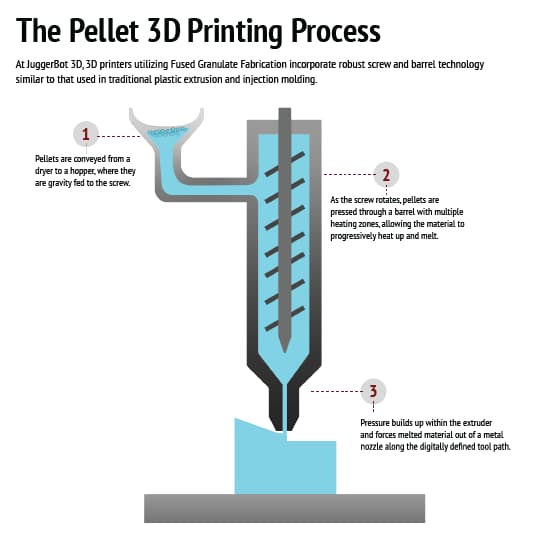
How the FGF Process Works
Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) employs a simple yet effective method. The process begins with 3D printing pellets, which are microscopic granules of plastic or composite materials. These pellets are fed into a barrel and screw extrusion system, which heats them to the melting point. The molten material is then forced through a nozzle and deposited in layers to make a component. This approach, known as pellet-fed additive manufacturing, allows for the rapid and efficient production of huge things. It varies from typical filament-based technologies in that it allows for the use of a wider range of materials while lowering material costs, making it suited for large-scale industrial applications.
Commonly Used Materials in FGF.
One of the primary advantages of Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) is its ability to process a wide range of materials. This versatility enables manufacturers to modify their goods to suit industry requirements, ranging from ordinary things to highly specialist pieces.
Types of Plastics and Composites
FGF may use a wide range of materials, including basic thermoplastics like as PLA and ABS, as well as more sophisticated composites. FGF makes components stronger and more durable by introducing fillers like carbon fiber or glass. This adaptability makes it an excellent alternative for industries that require high-performance components.
Recycled Materials in FGF Sustainability is a major concern in many businesses, and FGF is playing an important role in supporting environmentally sustainable manufacturing. FGF promotes the use of recycled materials in 3D printing, which helps businesses decrease waste while generating cost-effective, large-scale items. Businesses that use recycled 3D printing pellets can reduce their environmental impact while maintaining quality.
High-Performance Engineering Plastics
FGF is capable of handling high-performance technical polymers in demanding applications such as aerospace and automotive. These materials are exceptionally strong, heat resistant, and chemically durable, allowing them to tolerate harsh environments. This capacity enables the production of crucial parts using FGF that fulfill high industrial standards.
Applications of FGF Across Industries
Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) is altering several sectors by enabling pellet 3D printing. Its versatility to a wide range of materials, paired with its effectiveness in creating complex parts, making it a popular choice in a variety of industries.
Construction and Architecture
FGF is gaining favor in the building and architecture industries due to its capacity to manufacture big, unique components. From elaborate façade features to structural components, FGF offers architects and builders new design options. This technology shortens production deadlines, lowers material waste, and allows for the fabrication of distinctive architectural aspects that would be difficult to produce using traditional methods. pellet 3D printing in construction is changing the way we think about architectural design and fabrication.
Furniture and Art
FGF promotes creativity and individualization in furniture design and art. Artists and designers can create unique furniture, sculptures, and other artistic works with high precision. The use of pellet-fed additive manufacturing enables them to experiment with recyclable materials, composites, and high-performance plastics, pushing the limits of what is possible. FGF gives the resources required to create useful, beautiful, and sustainable designs on a bigger scale.

FGF vs. Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) and Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) have comparable 3D printing techniques, but they serve different objectives in manufacturing, especially when it comes to scale, speed, and cost.
Comparing Print Speed and Efficiency
FGF outperforms FFF in terms of print speed and efficiency, particularly for large-scale projects. FGF's pellet-fed method allows for faster material flow, resulting in much shorter print times. In contrast, FFF's filament feedstock restricts its pace, making it better suited to tiny items or precision work. When it comes to large-format additive manufacturing, FGF provides a more time-efficient alternative, making it excellent for organizations seeking to simplify production.
Resolution and Surface Finish
While FFF provides finer resolution and surface finishes due to the smaller filament diameter, FGF is soon catching up. Granulate extrusion technology advancements are increasing surface qualities for large-scale printing, but FGF remains best suited for applications where surface detail is less crucial. The continued development of FGF systems is expected to narrow the resolution gap over time, increasing their desirability for industrial applications.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
FGF really shines in terms of cost efficiency. FGF uses pelletized plastic feedstock to cut material costs, making it a cheaper solution for large-scale production. Its scalability also makes it a great contender for sectors that require manufacturing large batches of parts, giving both cost savings and production speed that that filament-based systems can't match.

Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Advantages
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in modern production, and Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) is emerging as a vital actor in this movement. FGF provides various eco-friendly benefits, establishing it as a sustainable solution in the realm of additive manufacturing.
FGF and Sustainable Manufacturing
FGF is designed to promote sustainable production. Companies that use pellet-fed additive manufacturing systems can reduce waste, optimize material utilization, and even include recycled 3D printing pellets into their manufacturing processes. This trend toward sustainability enables enterprises to reduce their environmental effect while maintaining performance and quality.
Using Recycled Pellets
One of the most notable benefits of FGF is its capacity to utilize recycled materials. Recycled pellets from various post-consumer or post-industrial sources can be melted and reshaped into new goods, lowering the demand for virgin plastics. This not only saves resources, but it also helps businesses meet sustainability targets, contributing to a circular economy in 3D printing.
Reducing Waste in Large-Scale Production
Large-scale 3D printing using FGF lowers waste by allowing for accurate material deposition. Traditional production methods frequently produce additional material waste, but FGF reduces this with its efficient extrusion process. FGF helps industries improve their sustainability efforts by minimizing waste while also lowering raw material expenses.
Energy Efficiency for FGF Processes
FGF also has more energy efficiency than other traditional production techniques. Granulate feedstock requires less energy to melt than filament-based systems, resulting in lower overall energy usage during production. This makes FGF a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for businesses trying to minimize their carbon footprint.
Best Practices for Scaling FGF Operations
Scaling Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) processes involves detailed planning and skill. To achieve successful large-scale production, producers must overcome numerous critical issues.
Technical expertise in material processing
Understanding material processability is critical for scaling FGF operations. Different materials, including 3D printing pellets and composites, necessitate specialized settings for best performance. Technical skill in controlling these materials guarantees continuous print quality and operating efficiency. Engineers must be knowledgeable with the properties of each material in order to fine-tune the extrusion process and get the required outcomes.
Testing Materials Before Full-Scale Production
Before committing to full-scale production, materials must be properly tested. This stage entails assessing how different pellets perform under various conditions to ensure they match the necessary criteria for strength, durability, and finish. Testing identifies potential faults early on and allows improvements to be made, reducing risks and guaranteeing that final products satisfy quality standards.
Future of FGF in Industrial 3D Printing.
Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) has a promising future as technology and material science develop. FGF is poised to play a critical role in the growth of industrial 3D printing, thanks to its scalability and efficiency advantages.
As technology advances, FGF systems are projected to increase in resolution and surface polish, narrowing the gap with Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) processes. Material science innovations will broaden the spectrum of granulate materials that can be used, including high-performance and environmentally friendly alternatives. Furthermore, the increased emphasis on sustainability will strengthen FGF's position as an environmentally aware manufacturing option.
FGF by LUSHI
Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) is promptly growing, with continuous advances in resolution and surface polish. Its primary advantages—cost efficiency, scalability, and sustainability—set it apart from other additive manufacturing technologies. FGF is raising the bar for industrial 3D printing by using innovative materials and streamlining manufacturing methods.
LUSHI uses FGF technology to create high-quality 3D printed solutions for furniture and sculptures, combining innovation and craftsmanship. As FGF evolves, it promises to revolutionize manufacturing techniques by providing efficient, environmentally friendly solutions that fit the needs of modern business.
